Easing labour market conditions are expected to encourage the Fed to deliver a third interest rate cut next month, even as progress in lowering inflation has stalled. Markets now see a 76% probability of a 25-basis-point rate cut by the Fed in December. Gold has plunged over $170 following the Republicans’ clean sweep in the election, as President-elect Trump’s proposed tariffs are seen as potential drivers of inflation. Investors eagerly digested remarks by Fed Chair Jerome Powell along with Friday’s retail sales data. Retail sales rose 0.4% from September to October, the Commerce Department said Friday, a solid increase though less than the previous month’s robust 0.8% gain.
US stock market experienced a slight pullback after the strong post-election rally. While the S&P 500 declined by approximately 2%, it still maintains a year-to-date gain of over 23% and a post-election increase of over 1%.
Gold
Gold prices fell and hit a two-month low on Thursday, driven by a strong dollar rally. Spot gold fell 0.1% to $2,570.05 per ounce, its lowest level since September 12. US gold futures settled 0.5% lower at $2,572.90. The US dollar index continued its upward march, making gold more expensive for overseas buyers. The Fed could possibly hold its cards close to the vest until the Trump administration and new Congress are in place and try to enact some of the policies discussed during the campaign and post-election.
Oil
Oil prices fell over 2% on Friday due to concerns about weaker Chinese demand and a potential slowing pace of Fed interest rate cuts. Brent crude futures fell by 2.09% to $71.04 a barrel, while West Texas Intermediate crude futures (WTI) fell by 2.45% to $67.02. China’s oil refiners processed 4.6% less crude than a year earlier in October due to plant closures and reduced operating rates at smaller independent refiners. The country’s factory output growth slowed last month, and demand woes in its property sector showed few signs of abating, adding to investors’ concerns over the economic health of the world’s largest crude importer.
US President-elect Donald Trump has pledged to end China’s most-favoured-nation trading status and impose tariffs on Chinese imports in excess of 60%, much higher than those imposed during his first term. Goldman Sachs Research economists have modestly lowered their 2025 growth forecast for China, following expectations of significant tariff increases under Trump. However, they would likely make larger downgrades if the trade war were to escalate further.
Oil prices also fell this week as major forecasters indicated slowing global demand growth. The International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts global oil supply to exceed demand by more than 1 million barrels per day in 2025 even if cuts remain in place from OPEC+. OPEC cut its forecast for global oil demand growth for this year and 2025, highlighting weakness in China, India, and other regions.
US retail sales increased slightly more than expected in October, suggesting the economy kicked off the fourth quarter on a strong note. Lower interest rates typically spur economic growth and aid fuel demand.
Inflation and Fed Policy
October’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) data aligned with expectations. Although inflation continues its downward trend, certain areas like shelter, rent, and motor vehicle insurance have not decreased as rapidly as anticipated. Nevertheless, there’s optimism that inflation will gradually approach the Fed’s 2% target in the coming months and potentially stabilize within a 2-3% range in the long term.
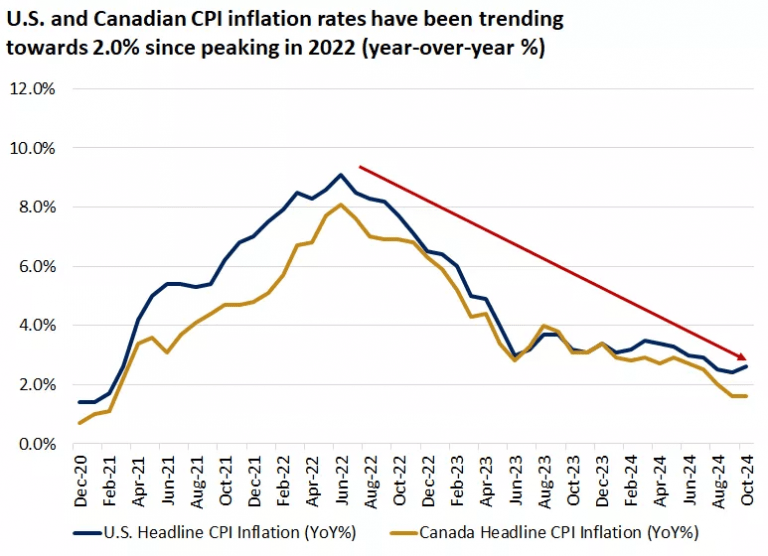
Inflation concerns persist in the US and Canada – Source: Bloomberg
Policy uncertainty, particularly regarding tariffs, has also contributed to market caution. While tariffs can negatively impact consumers, historical data suggests that their long-term inflationary effects are limited, especially for targeted tariffs.
The recent market pullback has provided an opportunity to assess the performance of different sectors. While technology stocks have been a major driver of the bull market, other sectors, such as energy and financials, have also shown strength. Investor behavior has also been influenced by a range of factors, including shifting risk appetites, changing interest rate expectations, and evolving geopolitical dynamics. As the market continues to evolve, understanding these factors is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
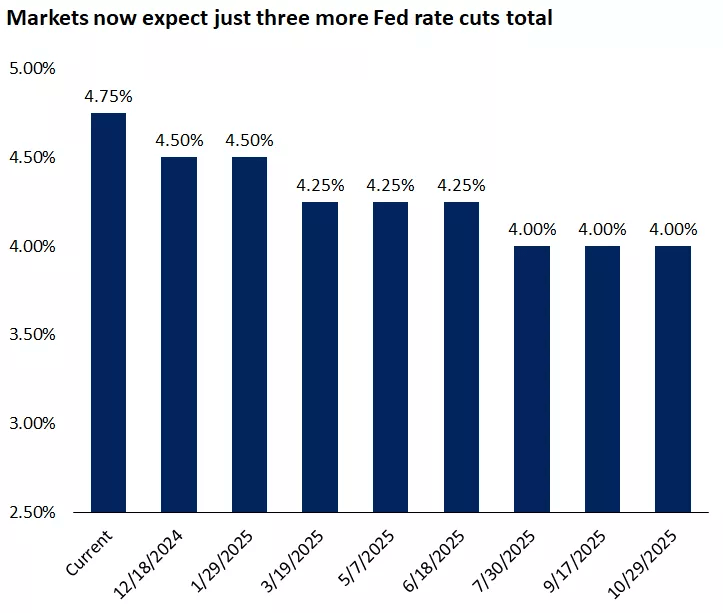
Rate Cut Expectations Through October 2025 – Source: CME FedWatch Tool
Cautiously Optimistic Outlook
Despite the recent market pause, the long-term outlook for the stock market remains cautiously optimistic. Strong corporate earnings, low interest rates, and accommodative monetary policy continue to support the bull market. However, investors should remain vigilant and be prepared for potential market volatility.
As investors get prepared for a historically strong period for financial markets, it’s important to note that some of the post-election gains may have been front-loaded. However, positive economic fundamentals continue to support the bull market. While policy uncertainty may lead to increased volatility, a resilient economy and contained inflation could help markets overcome these challenges.
Inflation: The Still Persistent Issue
October’s CPI and Producer Price Index (PPI) data highlighted persistent inflationary pressures, particularly in services. While headline CPI increased to 2.6% year-over-year and core inflation remained steady at 3.3%, certain areas like housing and rent prices remained elevated. While significant progress has been made since the peak inflation rates in 2022, the path to the Fed’s 2% target is likely to be bumpy. As economic growth moderates and the labor market eases, services inflation may also decline. However, as the economy potentially accelerates in the future, inflation may stabilize within a 2-3% range.
Tariff Uncertainty:
Tariff policies, while potentially inflationary, may have offsetting factors. Tariffs can lead to one-time price increases but often have limited long-term impact. Historical data, such as the example of washing machine tariffs, suggests that prices tend to normalize over time. Additionally, tariffs can incentivize supply chain diversification and domestic manufacturing.
Fed’s Stance: No Rush to Cut Rates
Fed Chair Jerome Powell indicated a more gradual approach to rate cuts, citing a resilient US economy and a healthy labor market. While the Fed may lower rates from the current 4.75% to a range of 3.5-4.0% next year, the primary motivation is to align the policy rate with the declining inflation rate.
A Seasonally Strong Outlook
The final months of the year are historically positive for the stock market. However, it’s important to consider that some of the post-election rally may have already priced in future gains. Nevertheless, strong economic fundamentals, contained inflation, and potential supportive policies position the market for continued growth, albeit at a potentially slower pace.
Global markets
The pan-European STOXX 600 index fell 0.5% on Friday, with technology and healthcare stocks leading the losses. The technology sub-index fell by 1.7%, with chipmaker ASML among the biggest losers. The weak forecast from US-based Applied Materials signaled sluggish demand for chipmaking equipment beyond AI-focused chips. Healthcare stocks were hit even harder, shedding 2.1%. Danish biotech firm Bavarian Nordic plunged 17% after reporting third-quarter core profits below expectations and forecasting weaker order volumes for 2025. European vaccine makers Sanofi and GSK also saw declines of 2.9% and 2.2%, respectively, after US President-elect Donald Trump announced plans to appoint Robert F. Kennedy Jr. to lead the Department of Health and Human Services. The Swiss market, heavily weighted with healthcare firms, also slipped by 0.8%. Market volatility was exacerbated by concerns over US-China relations, disappointing corporate earnings, and negative sentiment from a lower Wall Street close. Economic data showed Britain’s economy contracted in September, with slower third-quarter growth.
ECB
The European Central Bank (ECB) is facing a dilemma as it navigates a delicate balance between stimulating growth and maintaining price stability in the Eurozone. Recent rate cuts have raised concerns about the potential for a prolonged period of low inflation, with the September inflation data dropping below the ECB’s 2% target. While some policymakers argued that a sustained undershoot of the target was unlikely, others cited the sharper-than-expected decline in inflation and the risks associated with a weakening Eurozone economy. However, the release of October’s inflation data, which showed a surprising rise to 2%, has shifted the focus back to the economic outlook. With the global economic environment uncertain, the ECB is now facing increased pressure to provide further monetary stimulus. Analysts anticipate another rate cut at the December meeting, with the magnitude of the cut emerging as the key question. The ECB’s decisions will have significant implications for the Eurozone economy, impacting factors such as growth, investment, and employment.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin pulled back from near record highs on Friday as enthusiasm over a Donald Trump presidency waned, while overall market sentiment weakened due to rising uncertainty about U.S. interest rates.
The world’s largest cryptocurrency, which had recently climbed to unprecedented levels above $90,000 on speculation of favorable U.S. regulatory shifts under Trump, fell 2.6% to $87,634.6 Earlier in the week, it had reached a peak of $93,226.6. Investors are now watching closely to see if Bitcoin can cross the crucial $100,000 threshold. Despite Friday’s dip, Bitcoin is set to post an impressive weekly gain of around 14%, its strongest performance since late February. The cryptocurrency is also on track for its third consecutive week of gains.
The surge in Bitcoin has been fueled mainly by optimism surrounding Trump’s 2024 election victory. Significant institutional inflows into cryptocurrency-focused exchange-traded funds have played a key role in driving prices higher. Trump’s pledge to implement crypto-friendly regulations and even the possibility of establishing a national Bitcoin reserve have stoked investor confidence.
Key Economic Events This Week
• Conference Board’s Leading Indicators
• PMI Data
 Noor Trends News, Technical Analysis, Educational Tools and Recommendations
Noor Trends News, Technical Analysis, Educational Tools and Recommendations





